This past Tuesday evening, a large underwater earthquake happened off the coast of Honduras. This earthquake led to the Tsunami Warning Center issuing a tsunami advisory for Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands. While many people are familiar with hurricane season and some of the risks involved, tsunamis are less common. As a Weather Ready Nation Ambassador, we would like to make sure you are prepared and safe, no matter what mother nature may throw your way. Read on for information about these rare events and additional resources so you can be a tsunami ready traveler.
In This Post
Tsunami Information
What is a Tsunami?
When most people hear tsunami they initially think of a single massive wave that’s hundreds of feet tall. This visualization of a tsunami is popular in Hollywood for dramatic effect, but in real life such mega tsunamis are exceedingly rare. A tsunami is simply a series of waves caused by a large and sudden displacement of water in the ocean. Usually, this displacement is caused by an earthquake near the ocean floor, but anything that causes a sudden and large movement of water can trigger a tsunami. Other potential triggers include landslides, volcanic eruptions, explosions, and asteroid or meteor strikes.
Most tsunami waves are less than 10 feet tall when they reach land. This may sound minor, but the waves come in a series and often move at 20-30 miles per hour when they hit land. It only takes six inches of moving water to knock over an adult, and 2 feet of water can carry away most vehicles. Also important is the fact that tsunamis can be filled with a variety of debris. Unlike the typical wind driven waves seen at beaches, tsunami waves have no face and do not curl and break. Instead they are like a wall of water, carrying with it debris from the ocean, as well as debris from the land that washed back with a previous wave.
When and where do tsunamis strike?
Unlike other events, tsunamis do not conform to a typical “season” or region. A tsunami can strike any ocean coast and can even travel up rivers that feed into the ocean. The good news is that tsunamis are exceedingly rare. On average, two tsunamis hit land near their source per year. Approximately once every five years there will be a “distant” tsunami, or a tsunami that makes land fall more than 600 miles away from the source.
Since local tsunamis are more common than distant tsunamis, and earthquakes are the most common tsunami cause, the highest risk will be coastal communities that are near an active fault line. Earthquakes are hard to predict, but it is a good idea to know if you are traveling to an earthquake prone area. Most importantly, however, is to understand and respect the potential power of a tsunami. Don’t ignore them just because they are rare, and don’t be lulled into a false sense of security if you hear that the expected waves will only be a few feet high.
Understanding Tsunami Alerts
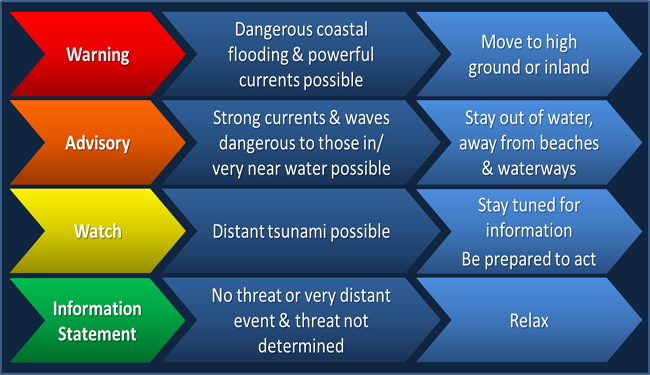
The Tsunami Warning Center issues three different levels of tsunami alerts. In order of severity these are watches, advisories, and warnings. Any of these alerts can be downgraded, upgraded, or cancelled as more information becomes available, so it is important to stay tuned for any updates.
Tsunami Watch
A tsunami watch means that there is the possibility of a distant tsunami. Typically with a distant tsunami, you will have a lead time of at least an hour, but you should be prepared to take action if you are near a coast. There is no need to evacuate at this point, but you should definitely listen for more information, and be ready to evacuate if it becomes necessary.
Tsunami Advisory
At this level, a tsunami is either expected or is already occurring. With an advisory there is the potential for strong currents or waves dangerous to those in or near the water. Flooding of the immediate beach and harbor area is possible. If you are in an area under a tsunami advisory it is important that you get out of the water and stay out until given the all clear. Even if there are no visible waves, strong currents and sudden tides can cause drowning. There is also a risk of debris in the water that can cause serious injuries. You should move away from the beach and harbor area until local officials give the all clear.
Tsunami Warning
If you are placed under a tsunami warning you should move to high ground or far inland. A tsunami warning is issued when there is a tsunami that is expected to cause widespread flooding. A large tsunami can cause significant flooding more than a mile away from the water. This flooding and dangerous currents can last for hours or days, so it is crucial to listen to local officials. Stay away from the water and coastal areas until the warning is lifted. There is no way to tell visually if another wave is coming or not.
Resources to Become Tsunami Ready
US Tsunami Warning System http://tsunami.gov/
NWS Tsunami Safety Information http://www.nws.noaa.gov/om/Tsunami/index.html
International Tsunami Information Center http://itic.ioc-unesco.org/index.php






